Page created on October 15, 2018. Last updated on December 18, 2024 at 16:56
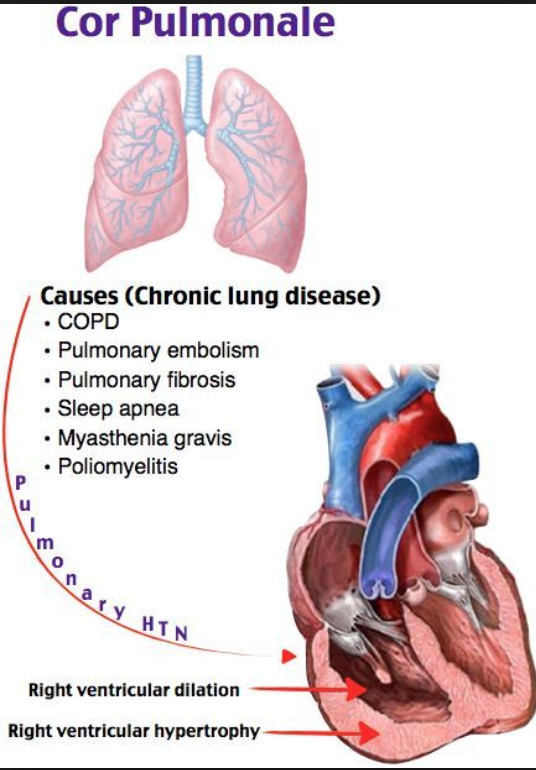
Chronic cor pulmonale has a slow onset and is caused by pulmonary hypertension due to primary disorders of the lungs or the pulmonary vasculature. The condition consists of dilative hypertrophy of the right ventricle, which often causes right ventricular failure. As a forward-failure symptom of right ventricular failure may left ventricular failure later also occur.
The causes for this to happen are many:
- COPD like, emphysema and chronic bronchitis
- Chest and spine deformities like pectus excavatus or scoliosis
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Chronic microembolization
- Pleural callus (pleural thickening)
The consequences are backward failure symptoms of right-sided heart failure:
- Systemic venous congestion – the venous blood accumulates in the circulation and viscera
- Hepato-splenomegaly
- Fluid accumulation in body cavities like ascites, pleura and pericardium (Pleural and pericardial effusion)
- Anasarca – effusion of fluid into extracellular space that make the skin swell.
- Nutmeg liver
- Induration of spleen
Cor pulmonale can also be acute, due to a pulmonary embolism.
See also the macropreparation.